___________________________________________________________________________________
Writers, if your crime scene includes skeletal remains or even remains that have advanced to a soupy mess, the person who is called in to take control of the bones is a FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGIST.
***NOTE: The forensic anthropologist is applying their post graduate studies in biology and anatomy as well as their understanding of trauma to research the bones. They do not solve the crime. They do not interview suspects or witnesses (LINK to Interrogation for Writers). They simply: study, document, report, testify (where necessary).
| Forensic anthropologists can help identify skeletonized human remains, such as these found lying in scrub in Western Australia, circa 1900–1910. (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Forensic Anthropology - Dem Bones!
Video Quick Study (3:13) Tanya Peckmann talks about her job.
| Servicemembers search for POW/MIAs on Wake Island Greg Berg uses a sifter to look for bone and artifacts at a dig site Jan. 12 on Wake Island. Mr. Berg, a forensic anthropologist, was sent to do a site survey after Wake Island officials notified the Joint POW/MIA Accounting Command of bones located on the island. JPAC officials are charged with achieving the fullest possible accounting of all Americans missing as a result of past conflicts. (U.S. Air Force photo/Tech. Sgt. Shane A. Cuomo) (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
* Remains are placed in a body bag for transport to a
forensic laboratory.
* The remains are reconfigured to a supine position, and
photographed.
* Any remaining soft tissue is cut away from the skeleton
* The bones are abraded with steel wool to remove dirt,
bugs, and soft tissues.
* The bones are then soaked in a chemical solution to
further clean and prepare them for examination.
This Video Quick Study (12:04) is a non-narrated look at a forensic anthropologist team at work
The Forensic Anthropologists attempt to make the first sets of identifying data:
* Approximate age
| FAFG - coded corpse (Photo credit: xeni) |
* Size/height
* Ancestry
AGE:
* Teeth and bone growth help to identify the proper age.
* Precise age determination is easier in children than in adults because of the statistical probability of various
developments taking place in teeth and bone fusion/growth plates.
* Age results for adult remains are given in broad ranges.
* 206 is the average number of bones of an adult.
* An adult skull has approximately 22 bones.
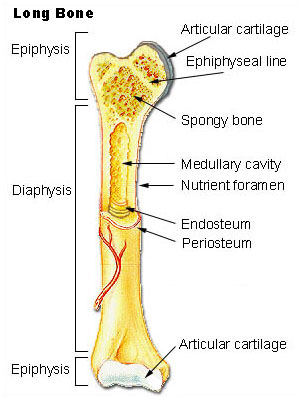
| Parts of a long bone (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
* In assessing age in children, the long bones of the body
show dramatic changes with age.
*ossification of the growth plates follow general
standards:
- First growth plates close at the elbow
- next ankles, knees, hips, then shoulders.
- The last growth plate to close up is the central tip of
the clavicle around 23-28. (health and nutrition
effects this age span)
Video Quick Study (1:48) - bone changes from infancy to adult
* At birth primary teeth are already present in the jaw.
* At 6 mos most infants have visible teeth.
Video Quick Study (3:17) Dr. Snow identifies Gacy's
victims by age.
| . (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
SEX:
* Prior to puberty, the skeletal remains cannot
be identified as male or female without DNA.
* A pelvis in a female is wider from front to back.
* Joints tend to be larger on males.
* Joints tend to be larger on males.
THE SKULL - this information is statistically correct. Measurements are made and compared at different points on the skull to determine a statistical probability rather than a 100% certainty.
* Male occipital protuberance is larger to attach larger
neck muscles.
* Male brow ridges are larger
* Women tend to have higher smoother foreheads.
* Male jaws tend to be at a 90 degree angle with
squared corners.
* Women's jaws tend to be smoother with
pointier chins
Video Quick Study (2:35)
* Male occipital protuberance is larger to attach larger
neck muscles.
* Male brow ridges are larger
* Women tend to have higher smoother foreheads.
* Male jaws tend to be at a 90 degree angle with
squared corners.
* Women's jaws tend to be smoother with
pointier chins
Video Quick Study (2:35)
| the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones. Except for the mandible, all of the bones of the skull are joined together by sutures, semi-rigid articulations formed by bony ossification, the presence of Sharpey's fibres permitting a little flexibility (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
SIZE AND HEIGHT
* Is best identified from a full skeleton.
* Statistics have been developed to allow a range based on skull size.
| the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones. Except for the mandible, all of the bones of the skull are joined together by sutures, semi-rigid articulations formed by bony ossification, the presence of Sharpey's fibres permitting a little flexibility (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
ANCESTRY
* Without DNA ancestry is difficult.
LINK to DNA article
LINK to DNA article
* DNA is best harvested from the teeth, though it is
possible to extract from bone.
* Skull structure yields the biggest clues about
race/ancestry based on math formulas.
* Few people today come from a racially pure
ancestral line, making identification more difficult.
* In order to apply the statistics to ancestral
identification, a fairly intact skull is required.
| Skeletons under excavation at Walkington Wold (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Beyond excavation (LINK to Crime Scene Info for Writers), and the preliminaries of age, sex, size and ancestry, a forensic anthropologist can offer investigators other identifying information:
* History of bone breakage
* History of surgical interventions such as ACL replacements and other injuries where screws and implants
were used.
* Nutrition over the life span
* Toxicity over time such as arsenic or mercury.
* Exposure to heavy metals like lead
* They can also help determine the number of skeletons in a mass destruction such as a large fire or plane
accident.
They can inform and testify about stab wounds and what type of weapon might have been used through trauma analysis.
* Was the break:
- antemortim trauma - before death like healed fracture or screws from surgical repair.
- post mortem trauma - what happened to skeleton after the death - like an animal
- perimortem trauma - bone damage at or around the time of death, such as a broken jaw or cracked
skull.
To gather this information they use CAT scans, and other medical diagnostic machinery.
Video Quick Study (3:51) Discusses high-tech tools.